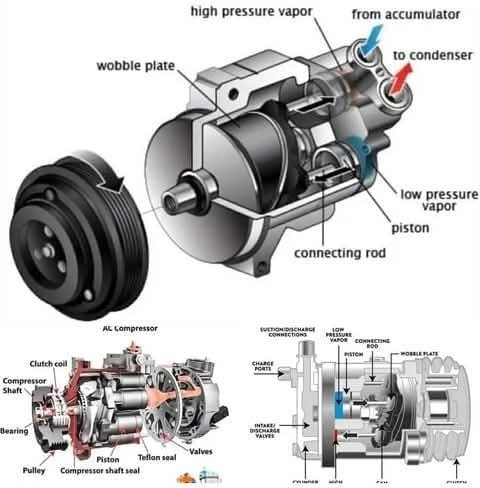
A/C Compressor: A Closer Look
This overview explains the components and functions of a swash plate compressor, commonly used in car air conditioning systems.
Key Components:
Swash Plate: Controls the piston's movement.
Connecting Rod: Links the piston to the wobble plate.
Wobble Plate: Transforms rotational motion into piston movement.
Piston: Compresses the refrigerant.
Cylinder Head: Houses the piston and valves.
Intake/Discharge Valves: Regulate refrigerant flow in and out.
Charge Ports: Allow refrigerant to be added.
High/Low Pressure Vapor: Represents refrigerant in vapor states.
Suction/Discharge Connections: Link the compressor to the A/C system.
Cam Rotor: Drives the wobble plate.
Clutch Assembly: Engages or disengages the compressor.
Accumulator: Stores liquid refrigerant.
Orifice Tube: Controls refrigerant flow.
Evaporator: Absorbs heat to cool air.
Condenser: Releases heat from refrigerant to the environment.
AC Compressor: The unit comprising all these components.
How It Works:
1. The cam rotor rotates, moving the wobble plate.
2. The swash plate tilts, causing the piston to compress the refrigerant.
3. Compressed, high-pressure refrigerant moves to the condenser.
4. The condenser cools the refrigerant by releasing heat.
5. The cooled liquid refrigerant passes through the orifice tube.
6. In the evaporator, refrigerant absorbs heat, cooling the air.
7. Low-pressure refrigerant returns to the compressor, repeating the cycle.
Benefits of Swash Plate Compressors:
Efficient and reliable performance.
Adjustable output to meet cooling needs.
Compact and lightweight design.